|
|
A
Little Bit More About Color |
 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Color Depth
Color "depth" is defined by the number of
bits per pixel that can be displayed on a computer screen.
Data is stored in bits. Each bit represents two colors
because it has a value of 0 or 1. The more bits per
pixel, the more colors that can be displayed. Examples
of color depth are shown in the following table:
Color Depth
1 bit color
4 bit color
8 bit color
24 bit color |
No. of Colors
2
16
256
16,777,216 |
Color Mode
Indexed Color
Indexed Color
Indexed Color
True Color |
Palette
Yes
Yes
Yes
No |
Determining Color Depth
Since each bit represents 2 colors, it is easy to work
out the number of colors for the various color depths.
The number of possible colors would be 2 to the power
of the number of bits per pixel:
A color depth of 4 bits would be 2 times itself 4 times:
2 x 2 x 2 x 2 = 16 colors
A color depth of of 8 bits would be 2 times itself 8
times:
2 x 2 x 2 x 2 x 2 x 2 x 2 x 2 = 256 colors.
A color depth of of 24 bits would be 2 times itself
24 times:
2 x 2 x 2 x 2 x 2 x 2 x 2 x 2 x 2 x 2 x 2 x 2 x
2 x 2 x 2 x 2 x 2 x 2 x 2 x 2 x 2 x 2 x 2 x 2 = 16,777,216
colors
True Color
Images are known as "True Color" where each
pixel is defined in terms of its actual RGB or CMYK
values. Every pixel in a a true color image has 256
possible values for each of it's red, green or blue
components (in the RGB model) or cyan, magenta, yellow
and black (in the CMYK model). Because there are 256
possible values for each RGB or CMYK component, then
RGB true color would have a 24-bit color depth and CMYK
true color would have a 32-bit color depth. There are
millions of possible colors for each pixel in a true
color image. That's why it is called "True Color".
RGB images are derived from the 3 primary colors of
red, green and blue. In 24-bit RGB color, each red,
green and blue component is 8 bits long and has 256
variations in intensity. These variations are represented
in a scale of values ranging from 0 to 255 with 0 having
the least intensity and 255 having the greatest. When
the 3 components are combined there are 256 x 256 x
256 possible combinations or 16,777,216 possible colors.
For example, white would be composed of maximum intensity
of red, green and blue light (R=255 G=255 B=255) and
black would be composed of zero intensity of red, green
and blue light (R=0 G=0 B=0). Cyan would be composed
of maximum intensity of blue and green light and zero
intensity of red light (R=0 B=255 G=255). Magenta would
be composed of maximum intensity of red and blue light
and zero intensity of green light (R=255 G=0 B=255):
True Color and The CMYK Color Model
Images using the CMYK color model are also true color.
CMYK images are derived from the 3 primary colors of
cyan, magenta and yellow plus black. In 32-bit CMYK
color, each cyan, magenta, yellow and black component
is also 8 bits long and has 256 variations in intensity.
Each pixel in a 32-bit CMYK image is one of 256 x 256
x 256 possible colors x 256 variations of black. A mix
of 100% each of cyan, magenta and yellow produces black,
so the black component is extra (more
here). Even though there are more bits per pixel
in the CMYK model, in reality it has a smaller color
"space" or gamut than RGB (more
here). Many graphics programs support both color
models.
Indexed Color
Images which do not define colors in terms of their
actual RGB or CMYK values and which derive its colors
from a "palette" are known as "Indexed
Color". The color palette of an indexed color image
has a fixed number of colors. Because the palette is
limited to a maximum of 256 colors, it is not possible
for an image to look as realistic as it can using RGB
or CMYK. Hence, they are not true color. This type of
color is known as "Indexed Color" because
colors in the palette are referenced by index numbers
which are used by the computer to identify each color.
Some file formats restrict the number of colors to fewer
than 256 . The GIF
format is one such format and has a color depth
of 8 bits per pixel or less. GIF files use indexed color
and allow a maximum of 256 colors. TIFF files can be
stored as indexed color or true color. A sample palette
is shown below:
Windows 16 Color Palette with
Index Numbers
 |
Grayscale Images
Grayscale images have a maximum color depth of 8 bits.
The reason for this can also be worked out easily. When
defining shades of gray in terms of RGB, each of the
3 red, green and blue components must be equal
to each other. Examples of grays are R=192 G=192 B=192,
and R=128 G=128 B=128. Since all three components must
be equal for any shade of gray there are only 256 possible
combinations. Thus, grayscale images have a maximum
color depth of 8 bits. A complete 256 color grayscale
palette is shown in the sample images below.
It is possible to create a grayscale image with a 4-bit
color depth or less. Some software packages allow the
user to reduce the number of colors in the palette from
256 to 16 or 2, though one would hardly classify a 2-color
image as grayscale.
 |
|
Note: The
palette images below have actual color values in
them. If you wish you can download them and save
them to your hard disk. |
| To download in Windows®: |
|
Right click image and select "Save
Image As..." |
| To download in Mac®: |
|
Drag image onto the Desktop |
|
|
Sample Images
|
Palettes
|
|
|
1 bit color:

|
2 color palette:
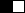
black and white |
|
|
1 bit color:
|
2 color palette:
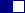
blue and white |
|
|
4 bit color:
|
16 color palette:


Windows 16 color palette
used for screen graphics |
|
|
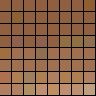
8 bit color:
 |
256 color palette:
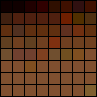 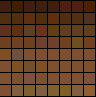 |
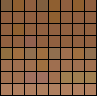 
|
|
|
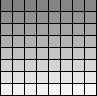
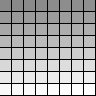
8 bit grayscale:
|
256 shade grayscale palette:
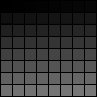  |
|
|
|
24 bit color:
 |
(No palette used) |
Spot Color vs. Process
Color
So far, all that has been described in this article
applies to computer displays. But what about printing?
What if you want to print a job without using process
color? What if you want to print a two or three-color
job? What if you want to use a special color ink such
as on a company logo? In this case use "spot color".
Spot color is the use of pre-mixed colors rather than
by combining color from cyan, magenta, yellow and black.
To ensure consistency of color the printing industry
has adopted standards for spot color. There are several
spot color systems but the most widely used is the PANTONE®
system. Pre-mixed colors are selected from swatch books.
These same color swatches appear in graphics programs.
When printing a spot color job, it is best to use PANTONE
colors to ensure consistency of color. However, you
may want to mix your own color for a company logo. In
this case have the printer contact his ink sales representative
and have the ink company formulate the color for you.
This service should cost little or nothing more than
the ink itself and can go a long way to establishing
that "special image" for your clients.
Many companies use a combination of four color process
and spot color in the printing of their product catalogs
and sales brochures. The photographs of the products
themselves are printed using four color process and
the company logo with a standard PANTONE spot color
or custom color. This would be a 5-color job. There
are many variations on this theme but the basic printing
methods are spot and process.
Click
Here To Continue...
|